
As internet technology goes through its next iteration with the Metaverse coming into its own in the past few years, there is a great deal of excitement in the tech world about its potential and possibilities.
With Metaverse gaining traction, developers and companies and finding novel ways of applying it to real-life use cases with the industry growing at an exponential rate.
Metaverse offers innovative opportunities in business functions such as remote collaboration.
Metaverse can address the challenges of remote work by providing a 3D virtual work environment where employees in their digital avatars could communicate and collaborate remotely with the team in real-time, ensuring productivity.
It also provides users with some semblance of real-life by connecting, interacting, and relaxing with peers in virtual meeting rooms and lounges.
Holoportation is a term that defines employees located in different parts of the world and collaborating in a virtual room. Metaverse allows users to be a part of holographic experience in a collaborative interaction in virtual meetings from different physical locations.
Metaverse also provides the right setting for different kinds of meetings, for instance, the ambiance of a basic meeting room would be different from a town hall meeting or a traditional conference room, or a training room. It allows users to create fit-for-purpose rooms where they can superimpose themselves in the virtual world and create the surrounding that is appropriate for their requirement.
Global enterprises like Nike, McDonald’s, YouTube, and Walt Disney apart from brick-and-mortar structures also have invested in virtual offices.
eXp World a cloud-based real-estate brokerage and technology platform, operates its entire business in the metaverse with employees and clients collaborating irrespective of their geographical location.
‘Viceverse’ is a metaverse-based headquarters created for the Vice Media Group in collaboration with the architecture firm Bjarke Ingels Group with meetings, briefing sessions, demos, presentations, etc. being held in this virtual office. Viceverse serves as the agency’s virtual innovation lab allowing clients to experiment with NFTs, DAOs (decentralized autonomous organizations), and Web 3.0.
Virtuworx offers a hybrid VR and MR environment with customization solutions to different requirement settings for events, offices, conferences, virtual training, and trade shows to users participating in their digital avatars.
Facebook Horizon’s Workrooms is another example of employees collaborating in the Virtual Reality space.
Metaverse has created a new and unique world full of possibilities and opportunities for a diverse variety of businesses. Although the early adopters might need to prepare for the challenges it presents currently, they will certainly gain a competitive edge by leveraging the immense potential of this field.
As internet technology goes through its next iteration with the Metaverse coming into its own in the past few years, there is a great deal of excitement in the tech world about its potential and possibilities.
With Metaverse gaining traction, developers, and companies and finding novel ways of applying it to real-life use cases with the industry growing at an exponential rate.
Metaverse offers innovative opportunities in manufacturing.
The metaverse has tremendous potential to transform the manufacturing industry as it exists today. The most obvious use case is that of digital twins – virtual replicas of physical entities – of the industrial and manufacturing spaces which offer users both a macro and a micro visualization of their plants and facilities. At an enterprise or macro level, it could offer a holistic and complete insight into the functioning of the organization in real-time. At a micro level, shop floor employees could use the metaverse space to monitor performance and identify and fix issues of individual equipment with its components, as if they were physically present there.
The world’s largest brewer, Anheuser-Busch InBev, is using the Metaverse to enhance its operations by using Azure Digital Twins to create breweries and supply chain digital models that are synced to the physical environment in real-time. The benefits of this archetype are fine-tuning the brewing process and quality control.
Research states that training in Metaverse results in students learning 4 times faster than they would in a traditional classroom environment.
The immersive learning process in the Metaverse has far better outcomes than in a traditional classroom setting and students learn better and faster in a VR environment.
Training in the Metaverse environment for the manufacturing industry implies safe and risk-free training in a safe virtual environment. In a real-world environment, an apprentice undergoing training with heavy physical equipment might face risks in a potentially hazardous setting.
Companies like JetBlue use VR technology to train their technicians. A real-life scenario of training technicians with real aircraft would be expensive and time-consuming and potentially risky. The company used VR sets for its technicians and in collaboration with Strivr deployed a solution that simulated a real-life setting and eliminated the time, expense, and risk of a physical environment. Also, training in a VR metaverse allows a trainee to make mistakes in a secure environment without undesirable consequences.
The Engineering and Aerospace conglomerate, Honeywell, uses AR and VR in its training efforts. VR and Mixed Reality can be used to provide remote assistance and collaboration in the resolution of complex repair and maintenance issues. Technicians in the BMW facility use AR glasses to provide a hands-free video overlay and at the same time connect with support teams sitting many miles away to fix the issues.
Manufacturers can also benefit from Metaverse simulations of their facilities to test possible factory scenarios which will then enable them to develop methods to automate and optimize their plants. Before creating its actual factory in Bavaria, BMW in its virtual factory, replicated its complete production workflow digitally to ensure that all processes were optimized and operated smoothly.
Metaverse can benefit manufacturers by facilitating improved consumer decision making too. For e.g.: automotive manufacturers can enable prospective buyers to “touch and feel” a car and even customize it to their tastes before they buy it. This simulation and visualization of the actual car help manufacturers understand the customer’s requirements the first time and minimize the effort and expense involved in rework. The metaverse can help car dealerships by facilitating test drives from the comfort of a prospective customer’s home, helping sell cars, and broadening the dealerships’ reach. Opportunities in this space include establishing a virtual dealership for customers to ask the dealer questions about their vehicles, take a test drive, or even just view vehicles.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution has created a world of online and offline convergence with the manufacturing industry being a major part of it. The industrial metaverse aims to bring digital experiences to inherently physical processes, taking digital transformation and “Industry 4.0” to a new level. The industrial metaverse starts with a digital experience before translating it to physical operations, rather than using IoT or building digital platforms to bring machines online. This is useful in areas such as predictive maintenance and asset monitoring and can be done remotely. The metaverse also offers significant advantages in Industry 4.0 regarding training employees and accessing data.
Metaverse has created a new and unique world full of possibilities and opportunities for a diverse variety of businesses.
Although the early adopters might need to prepare for the challenges it presents currently, they will certainly gain a competitive edge by leveraging the immense potential of this field.
As internet technology evolution goes through its next iteration with the Metaverse coming into its own in the past few years, there is a great deal of excitement in the tech world about its potential and possibilities.
With Metaverse gaining traction, developers and companies are finding novel ways of applying it to real-life use cases facilitating the industry’s growth at an exponential rate.
The Metaverse offers innovative opportunities to businesses. Here are some use cases where it can favorably impact the healthcare delivery model in the following areas:
Telepresence
Metaverse in healthcare has introduced new avenues for offering treatments at subsidized rates and in geographical locations that health providers may not be able to visit through telepresence. Virtual 3D clinics offer an easy and convenient way for patients and doctors to interact with each other. They are especially effective in the case of minor health conditions where a doctor could diagnose a patient without any physical examination and all that is needed is for the patient and doctor to have headsets.
Mental health is another area where metaverse could prove beneficial. Through immersive VR experiences, psychiatrists could treat disorders like PTS (post-traumatic stress), Anxiety, Delusions, Eating disorders, and so on.
gameChange is a landmark Virtual Reality Therapy that treats patients who suffer from psychosis – it targets the extreme anxiety that keeps patients from participating in day-to-day activities. The trial results showed that the treatment was effective and extremely popular among patients with high uptake rates.
Decentralized storage through Blockchain
Blockchain is a key technology that drives the metaverse. The management and security of highly sensitive and valuable health data is the most significant application of Blockchain in healthcare. Blockchains allow for data to be stored securely through decentralized, distributed, and encrypted databases. When a patient’s health records are stored on a blockchain, it makes them difficult to hack. They are also easily accessible when a patient gives consent to a doctor to review his records just with the click of a button.
Digital Twins
Digital twins are virtual models or simulations of any process, system, or object that generate real-world data with the purpose of learning more about the real-world counterpart. In the metaverse, Digital twins can be used to create ‘test dummies’ for individuals which can be used to predict outcomes, e.g.: response to specific medications, recovery from surgery and illness, and so on. Med-tech companies like Siemens Healthineers and GE Healthcare are investing in digital twin technology.
Precision Surgery through AR/VR
Immersive Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and AI technologies are helping surgeons to perform minimally invasive and more precise surgeries by getting a 3D view of the patient’s body which helps them to plan and perform operations.
Moreover, the data gathered from the patient’s digital twin will help them to predict recovery duration, possible complications, and prescribed treatments if complications arise post the surgical procedure.
Zimmer Biomet’s OptiVu Mixed Reality platform uses Microsoft Hololens2 to offer a mixed-reality world that offers innovative solutions to streamline surgical planning and workflow and offers real-time support that enables surgeons and care teams to collaborate and improve patient outcomes.
Training
Traditional medical training offers limited resources for the practice of surgeries partly because dissection procedures on cadavers prove to be costly for hospitals. With VR, students can train in a simulated environment at a significantly lower cost.
Dissection on a virtual cadaver improves learning outcomes as it enables students to work individually. It enhances students’ technical capabilities such as precision and decision-making skills and is cost-effective too.
Collaboration
Instant sharing of information between doctors and support staff will ultimately lead to quicker diagnosis and quality healthcare service.
Veyond Metaverse offers XR technology solutions that augment and improve medical education and training, surgical planning and procedures, and diagnosis and treatments through its proprietary cloud communication platform.
Metaverse has created a new and unique world full of possibilities and opportunities for a diverse variety of businesses.
Although the early adopters might need to prepare for the challenges it presents currently, they will certainly gain a competitive edge by leveraging the immense potential of this field.
The internet was created without a native identity layer and different Internet solution providers have developed ad hoc identity solutions that are inconsistent. With billions of people now online, the drawbacks are more apparent, more so with the emergence of Web3. Decentralized Identifiers (DID) are globally unambiguous identifiers that can be used to identify any subject (e.g., a person, an organization, a device, a product, a location, or even an abstract entity, or a concept) and enable secure online transactions. DID is a new type of verifiable identifier, which does not require a centralized registry. DID enables the controller to verify ownership of the DID use cryptography while ensuring security.
W3C Decentralized Identifiers are portable across service providers and can last for as long as their controller wants to continue using them. DID can also be used as a tool to verify professional documents, including passports and driver’s licenses. Users can securely navigate across a variety of platforms with DID with a consistent identity for their wallet and personal information.
DID solutions can help uphold the integrity of users’ data and provide new safeguards for users. They can verify identities, authenticate traceability, validate digital assets, and enhance the overall security of the internet. DID applications can help users successfully control and manage their own digital identities, where they can log in securely to different systems without exposing their privileged information.
The decentralized identity market size is expected to grow from USD 285 million in 2022 to USD 6,822 million by 2027, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 88.7% (Source).
Additionally, one-click login & onboarding with identity verification was the application that most people (57%) felt the need for decentralized digital identity among Web 3.0/DeFi implementations in a 2021-22 survey (Source).
Web3 requires a critical degree of security throughout the ecosystem to ensure its full potential so that every transaction is accurately recorded and cannot be altered. Without DID solutions, there is a risk of users losing their sensitive valuable, and confidential information to hackers and fraud.
The adoption of crypto and advancement across Web3 has increased rapidly but there are still significant barriers that stand in the way of mainstream adoption. DID can address some of the current Web3 pain points related to:
Nonfungible tokens (NFTs), Identity and Authenticity issues, fraud, and plagiarism threats affect artists or creators. An example is a work of digital artist Derek Laufman (designer of Marvel superhero stories) being auctioned on NFT platform without his knowledge. To counter such issues, applications can be built on DIDs to allow creators to prove that a given NFT was created by them. Buyers and sellers can verify the authenticity of digital artwork.
Growth of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) – Collateral requirements limit most cryptocurrency traders looking to take advantage of leverage. Reducing or completely removing collateralization requirements would enable mass adoption of DeFi. The DID layer can provide users with credit-based loans and help users directly control their own credit scores, better monitor, and adjust their own lending behavior. So far the identification has been issued by the government. With DeFI we need a global level of identification and KYC.
KYC and other identity controls could change DeFi by allowing regulated entities to participate as intermediaries, directly and indirectly. DeFi protocols could enable trusted third parties, like identity providers, to perform the KYC.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) use token-based governance for voting, governance, or prioritization but it can preclude or de-prioritize active contributors without significant capital. Each DAO member of the hundreds of DAO needs to build their reputation within, only through participation. DIDs can help users maintain their reputation across multiple DAOs. Porting credentials from one DAO to another is easier with DID.
The DID specifications are based on foundational pillars. DID metadata is resolvable and can be discovered. DID are:
The DID ecosystem is made up of layers, with each layer on the top, building upon the underlying protocol. It includes:
W3C Decentralized Identifiers and W3C Verifiable Credentials are used across several markets where identification and data authenticity are a concern:
The Retail and the E-commerce sector have seen rising digitalization, outlining the need for increased authentication given the complexities in data systems. Convenience stores, grocery stores, restaurants, bars, and consumer goods companies can use DIDs for new digital age verification programs to increase privacy and checkout speed, prevent unauthorized data access, reduce data losses and eliminate the use of fraudulent identity documents during purchase.
The Financial Services industry depends on identity verification to check illegal activities such as bribery or money laundering. DID can help refresh KYC processes by allowing for the effective outsourcing and decentralizing of personal data, while also allowing the owners of the data to retain full control over it. DID can help in the shopping and purchase of insurance products, finance and credit products, e-finance, and cross-border remittance.
According to Forbes, major banks each spend up to USD 500 million on cybersecurity every year, with USD 25 billion being spent in the US on AML compliance. Source
Governments – Government agencies in the US, Canada, and EU are exploring the use of DIDs to provide privacy-protecting digital identity documentation for their businesses and residents, enabling them to choose how and when their data is shared.
Supply Chain operators and stakeholders such as global government regulators, trade standards institutions, vendors, shippers, and retailers use DIDs to design systems that verify the origin and destination of products and services accurately. This will streamline and enable the reporting and documentation to apply correct tariffs, prevent dumping, and monitor transshipment.
Personnel and Workforce – Universities, education standards organizations, and training programs use DIDs to issue digital learning credentials when applying for higher education or workforce positions.
Being a key technological foundation to support native Web3 applications, World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) has declared that Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) v1.0 is an official Web standard. This verifiable identifier enables both individuals and organizations to take greater control of their online information and relationships while also providing greater security and privacy.
Robust DID solutions can help Web3 to go mainstream by enabling new use cases. The composability and interoperability of DID standards help the momentum created from each new application feed on another. DID solutions having been declared an official standard by W3C we expect it to grow rapidly in the coming years. The presence of service providers can unlock the next major cycle of Web3 applications and the value therein.
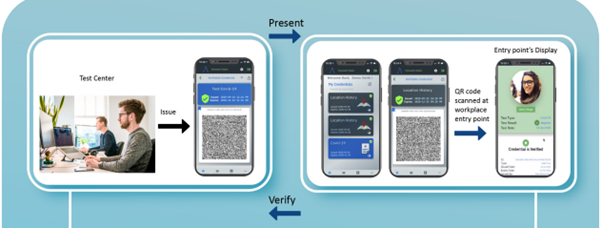
Chainyard has firsthand experience in building to W3C DID standards. The health wallet app is an example of its capabilities in this space while its use cases provide detailed insights about its projects along with sample UI/UX development. Chainyard is an innovator in blockchain and distributed ledger applications, and the owner and creator of Trust Your Supplier. The first Chainyard initiative in this space is the innovative MyHealth Wallet application, available on Android and iOS. It provides the user with a simple, tamperproof, and verifiable way to present and prove that they have taken a COVID-19 test.

The second in the family is the Trusted Health Checks mobile application that combines human validation and ML-generated risk scores and allows visitors to complete electronic health declaration forms prior to travel to foreign destinations.
Metaverse is a three-dimensional virtual world on the Web offering users an immersive experience where they interact with each other through their virtual avatars on various levels to do business or meet socially akin to our real physical world.
The history of the metaverse reads like a classic tale of life imitating art. The term Metaverse first appeared in the Sci-fi novel ‘Snow Crash’ by author Neal Stephenson in 1992 as a blend of words “meta” and “universe”.
However, it became the center of attention in recent years after Facebook, now Meta, and Microsoft announced several projects around it.
The global Metaverse Market size is estimated to reach USD 426.9 billion by 2027 at a 47.2% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR). The market for metaverse was valued at USD 61.8 billion in 2022.
So, what makes Metaverse a path-breaking technology? The answer lies in its capabilities and features.
The Metaverse is seen as an infinite world that keeps expanding and to enable this expansion, a high-speed, interface with low latency, and scalability, is required. This robust infrastructure is the mainstay for a seamless and rich user experience.
Immersiveness is the sense or the illusion that the user experiences, being present within the content rather than observing it from outside. Supporting this immersive experience are the Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and XR (Extended Reality) technologies.
Digital Avatars are key components of the Metaverse blueprint and digitally represent the users in the virtual world while gaming, shopping, working remotely, learning, and socializing. They significantly reinforce the interactive and immersive user experience in Metaverse.
Just like the real world, the Metaverse goes on and on and never rests. So, even if the user takes the VR headset off, this world persists.
Security is a vital feature in the metaverse, and ethical and privacy standards have been laid down to address cyber security concerns for the metaverse.
The Metaverse is still in its early stages, and the concern for security cannot be overstated as it needs high standards for user protection and user identities. Adherence to these standards will enhance user confidence and subsequently lead to more and more users adopting this world with robust user protection and hackproof user identities.
A thriving virtual economy drives the Metaverse and is largely built on cryptocurrencies like MANA, Sand, Ethereum, digital currencies like Robux, and digital goods and assets like nonfungible tokens (NFTs). Examples of NFTs include apparel, accessories, and works of art.
Underlying the rich and immersive Metaverse experience are cutting-edge technologies like Web 3; Blockchain; VR, AR, and XR; IoT; and AI/ML. Their specialties are:
The common challenges in a metaverse world include:
One of the main challenges is the vulnerability of data, as there is a huge amount of critical personal data that is transferred in the metaverse and could lead to its sale to interested parties by cybercriminals. The use of VR and AR headsets can cause privacy breaches where users’ personal data is compromised. The headsets come with camera capabilities and software that are vulnerable to hacking.
As of now, there are no universal guidelines for regulations in the Metaverse, and the privacy of the users depends on the metaverse platform and property owners. Cybercriminals in the Metaverse can easily impersonate a user by spoofing their identity and taking on their 3D avatar to commit fraud and cause damage to the user’s reputation.
The challenge of whether the person that the metaverse users are interacting with is genuine or not will always persist.
Metaverse may have an adverse effect on human relations with users choosing the virtual world over the real one. This results in fewer physical interactions in the real world and the virtual world becomes a haven for people who do not want to cope with the challenges of real life.
It can also lead to addiction issues, like gaming addiction. In fact, the issue may be compounded due to the immersive nature of the metaverse with kids and teenagers being most at risk. Users of this age group may also find it difficult to balance time between the real and the virtual world.
Interoperability is the ability to bring together various metaverse platforms, economies, and avatars under one umbrella.
With major players like Microsoft, Meta, and Apple investing massively, it is unlikely that we will see a unified Metaverse. The lack of interoperability might limit users’ access to the various metaverse platforms as different platforms might need different hardware for the users to enjoy an immersive experience. Moreover, questions arise about the possibility and ease of users traversing different metaverse platforms.
Just like HTML is the unifying protocol that allows users to access the internet from any browser, a similar protocol that enables movement and is compatible across devices is needed to traverse the metaverse.
As it is still early days for the Metaverse, the question of digital assets, and their ownership is still unclear as is the use of avatars in representing users as their digital twins could give rise to legal and ethical issues.
For instance, when avatars representing users interact in the Metaverse resulting in an altercation or even worse, an assault then what are the criminal laws that need to be applied to such a situation? These kinds of issues need regulations and laws in place to protect the avatar’s rights in the metaverse. This implies assigning a legal persona to an avatar with rights that allow them to sue and be sued.
The more difficult and thought-provoking issues are establishing standards and criteria that differentiate a legal avatar from the real-life person who owns the avatar.
With the Metaverse being touted as the next iteration of the Internet, enterprises will need to plan and strategize for its multiple challenges.
The Metaverse still has a long way to go and what appear as challenges today might well be opportunities that companies and users could leverage to their advantage.
Real estate tokenization enables the modern-day concept of fractional real estate ownership. Additionally, it helps overcome investment barriers and reduces associated risks and costs. Solution providers in this domain help real estate investors navigate through the various stages of – Deal Structuring, Legal Structuring, Technology (e.g., blockchain), Distribution, and Marketing.
The following infographic provides a snapshot of the current market, its potential, and expectations, along with the process, benefits, challenges, and solutions.
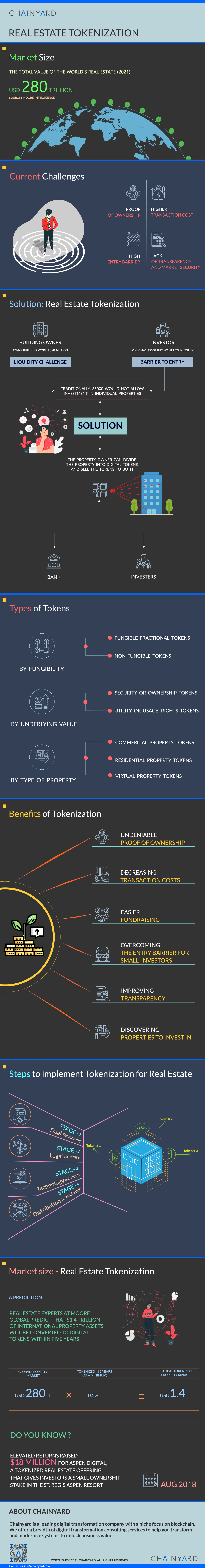
Read more here:
Transforming the business of Real Estate Assets through Tokenization
Real Estate Tokenization: Implementation Process Steps and Key Outcomes
In the article titled “Transforming the business of Real Estate Assets through Tokenization“, we have summarized various types of real estate tokens, the challenges it solves, and areas one needs to be aware of when venturing into them. This article focuses on the real estate tokenization process and implementation.
The real estate tokenization process starts with two steps – identifying the deal type and defining the legal structure. Subsequently, implementation involves selecting blockchain technology for storing tokens and choosing a platform where investors can securely purchase digital assets after verifying KYC and AML requirements.
The process begins with deciding on the asset kind, shareholder type, jurisdiction, and relevant rules that have a crucial impact in this initial phase of structuring deals. Generally, issuers choose to tokenize an existing deal in order to provide liquidity to present investors before soliciting money for a new project. Asset owners determine the specific property (or properties) to be digitized. The key considerations in deal structuring would be time-period for ROI, cash on cash return, securing investments, and legal and business formations. These more important details along with specific features/ parameters like rental type, rent start date, neighborhood, year constructed, stories, bedroom/bath, and total units are considered in the process.
The ownership information recorded on paper is transferred to the blockchain during the digitization stage. Security tokens are stored in a distributed ledger, and various actions are encoded in smart contracts. A legal wrapper needs to be created over the individual property to securitize and form an investment vehicle; a step necessary to digitize real estate.
The most common structures are:
Real Estate Fund: A private equity firm invests in a portfolio of properties, and the token symbolizes fund units. Accredited investors or approved institutional purchasers may only leverage the dividends gained from the tokenized investment.
Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT): Investors can create digital shares in a REIT, and token holders have the same rights to the REIT’s operational revenue that traditional investors do today.
Project Finance: Tokenization is a highly effective method of generating funding for projects. Tokens are made available to consumers and accredited investors during this event. Here the token may represent the ownership or future right to use.
Single asset Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV): Tokens represent shares of the SPV under this arrangement, usually a series LLC, for compliance with KYC/AML rules for LLCs, each token investor needs to be registered as a member of the LLC before investing.
After defining the legal structure, the next step is to choose the right technology. The process involves making four choices:
Selecting Blockchain / Token: This involves, choosing the Blockchain on which the token will be recorded, deciding on the token standard to be used, modeling the token data, and defining smart contracts to establish rules on transfer, limits, commissions, etc.
Primary / Secondary Marketplace: Choosing how initial tokens will be mined and provided during the initial offering and defining where and how investors will trade the tokens later.
Custody: Establishing a secure custody system for real estate, including proper maintenance and reporting of real-world updates.
KYC/AML: Verifying investors within regulatory compliance on a periodic basis.
The token generation and distribution are the primary focus of this stage, where several payment options are offered when purchasing tokens. Investors may require a digital wallet, available on the web and mobile platforms, to store the tokens. Investors receive these tokens during a live sale.
Primary Distribution: Tokens are awarded to the investors through this procedure in return for investment capital this is also the first time the tokens are minted.
Post-Tokenization Management: This step includes processes for managing corporate activity, such as shareholder voting and dividend distribution. Smart contracts coded on the token can automate these procedures. Management of the tokens will continue after they have been issued until they reach maturity or redemption.
Secondary Trading: Tokenization increases liquidity in secondary trading. A token holder can swap tokens with another investor on a marketplace, through an exchange, or over the counter.
Real estate tokenization has several advantages that make it a far more efficient investment option than any previously available ones.
We can expect Real Estate Tokenization to open the market for real estate assets enabling efficient movement of the funds and effective management of equity besides providing higher reliability, transparency, and security. Real estate tokenization would be the future of real estate assets with Blockchain technology as the underlying foundation and platform making it more robust, flexible, and secure when compared to the traditional models.
Given these advantages, it is no surprise that the RET market is estimated to become a $1.4-trillion market by 2026 (source). This potential can be fulfilled provided the technology is optimized to overcome existing hurdles and issues. Additionally, expert solution providers in tokenization have an important role in expanding the market and helping real estate players navigate the initial stages of tokenization and minimize the risks and costs associated with it.
Chainyard has vast experience in architecting, building, testing, securing, and operating blockchain-based solutions for some of the largest companies in the world in multiple domains: Supply Chain, Manufacturing, Transportation, Logistics, Banking and Trade Finance, Insurance, Healthcare, Retail, Government and Procurement. Read these customer success stories to find how Chainyard helped clients build enterprise-grade large blockchain-based technology solutions. Chainyard is instrumental in building a platform for procurement innovation, Trust Your Supplier, that enables suppliers to create and maintain a trusted digital identity and selectively share information with a vast network of buyers and partners. Read more here.
The Value of NFTs and Their Impact on Blockchain
Non-fungible tokens, or NFTs, haven’t changed the blockchain industry at its core. However, they’ve had quite a positive impact on bringing more visibility to blockchain and its many uses.
Many people not involved in the blockchain industry have been introduced to NFT crypto-assets in the form of digital art. Although collectible art is certainly one use for these assets and their unique attributes, it’s just one representation of the vast array of ways thatNFT and blockchainsolutions could change modern life.
For example,NFT ticketswould help cut down on counterfeit sales for sporting events, concerts, conventions, and more. Because NFTs can’t be duplicated, the originals would be simple to verify. Plus, each NFT ticket could be programmed via a smart contract to entitle the legitimate ticket holder to special perks like free merchandise or exclusive gatherings.
NFTs are also heating up the video game industry, which shouldn’t be a surprise. Many players would like to own the digital assets they purchase or earn while moving through a game. Using an NFT-in-game premise, those players could retain ownership of any assets beyond the confines of the game. This would enable them to market or sell those assets for a profit later.
Real estate is yet another growth space for the NFT industry.Saving land contracts on NFTs can reduce crimes related to fabricated documents. Perhaps one day,NFTs for landinformation will lessen the need for costly legal intervention in cases of proving who owns which parcel.
The Multifaceted Value Proposition of Blockchain and NFTs
Of course, many people still aren’t sure what makes NFTs particularly valuable. Even those who understand NFTs generally have a little trouble seeing their real-world applications.
So what is the value of an NFT? Below are some of the major reasons NFT and blockchaintechnology stir up so much discussion surrounding profitability and inherent value.
1. NFTs offer provenance and ownership.
Because the token (a.k.a., the NFT) on a blockchain can’t be forged or 100% duplicated, it becomes its own authority. Someone who owns an original NFT doesn’t need to go through a central authority to show the NFT’s authenticity. Removing the need for someone in the middle to legitimize an NFT makes ownership and trading less cumbersome. Accordingly, the value saved is transferred to the value of the NFT.
2. The NFT industry is fostering buyer-seller efficiencies.
More and more, NFT holders can tap into global marketplaces when they want to sell their NFTs. Because NFTs have more liquidity than traditional assets, their holders can recoup investments more readily. Additionally, NFTs support fractional ownership, giving smaller investors access to larger investments by enabling them to own a “slice” rather than an entire asset.
3. Smart contracts can follow NFTs for life.
NFTs can be programmed with smart contracts. Consider the situation of a digital artist who programs an NFT with a smart contract. The smart contract may give the artist a percentage of any sales of the NFT. Consequently, every time the NFT changes hands, the smart contract terms would be enforced immediately.
4. Blockchain and NFTs offer decentralization with security.
By its very nature, blockchain requires none of the centralized entities controlling the markets and marketplaces the world currently relies on. Rather, blockchain and NFTsfoster decentralization and transparency. At the same time, they offer incredible levels of security that would have seemed unfathomable before the advent of blockchain ledgers.
5. NFTs build trust that’s often missing in transactional relationships.
Blockchain ensures a single version of the truth. Period. As a result, systems and assets like NFTs that are built on blockchain are trustworthy. Any transference of blockchain items can be handled with a high degree of trust. And again, there’s no need for a centralized authority to step in to fuel the trust factor. It just exists.
To be sure, NFTs — and blockchain, for that matter — are going through what can only be called the “hype” cycle. Very high expectations are being set for what blockchain and NFTtechnology can and will do. No doubt, some people will be disillusioned along the way to blockchain’s maturity. Nevertheless, blockchain and NFTs are positioned to have a significant and transformative effect on many industries beyond those that have tested the waters so far.
Real estate tokenization is a modern-day extension of traditional fractional real estate ownership. It is like crowdfunding in that it distributes the value of a real estate investment into manageable segments to overcome many investment barriers. Each token represents one part of the asset. Each of these tokens is then encrypted with the relevant details, which gives the investor the ownership details based on their share of the property. It is now possible to buy and sell these tokens at their determined value on a secondary exchange.
Global Real Estate Tokenization Market size is expected to triple in 5 years from 2022 to 2027 (Source)
However, with real estate tokenization, it is easy to find more new investors since assets can be fractionalized. Moreover, investments and transactions are more secure, authentic, and reliable. Real estate players can now leverage tokenization as one of the primary sources to raise funds for their projects.
Despite the Blockchain and Tokenization technology are getting matured, regulations are still lagging There are several challenges due to this, including:
Real estate tokenization on distributed ledgers has the potential to revolutionize the way common people invest.
Being in its early stages, tokenization needs to overcome several concerns to achieve its full potential and requires the effort and contribution of technology companies to make the innovations and set in motion the processes. Companies like Chainyard can help navigate the early stages of tokenization to minimize the risks and costs associated with this technology that carries immense potential.
In the upcoming blog, we will also be covering key processes involved in real estate tokenization, the benefits of real estate tokenization, and how Chainyard can help you in this journey of tokenization.
Originally published at International Business Times. Read the full article.
A token is a digital twin of a physical object or service in a blockchain that provides undisputed ownership and provenance, reduces transaction costs, and enables transaction automation through smart contracts.
A token can represent anything – a character in a game, airline ticket, work of art, coins, etc.
Real estate tokens, digital artwork, fashion, licenses and certifications, capital markets fundraising, sports moments, virtual worlds, gaming, and crypto collectibles are just some of the thriving use cases in tokenization.
The key messages are:
The benefits of tokenization, especially fractional ownership, transparency, increased liquidity, and improved security, create new opportunities for improving the value transfer systems.
New tokens are being created every day, from physical assets to intellectual properties.
Want to learn more about how tokenization is disrupting the financial industry. Talk to an expert.
